MobiTang
Mobil widget interaction using signal processign and machine learning.
The proliferation of touch screen technology in various consumer electronic devices such as smartwatches, smartphones, and smart TV controls has presented a number of challenges related to the utilization of flat touchscreens. Most notable of these challenges is the ”fat finger problem” which obstructs content on the screen. Additionally, there is a lack of controls in certain applications, such as video games, necessitating an innovative solution. To address these issues, this proposed research endeavors to prove validity of physical widgets that can be attached to smartphones, providing supplementary control options through various interactions.
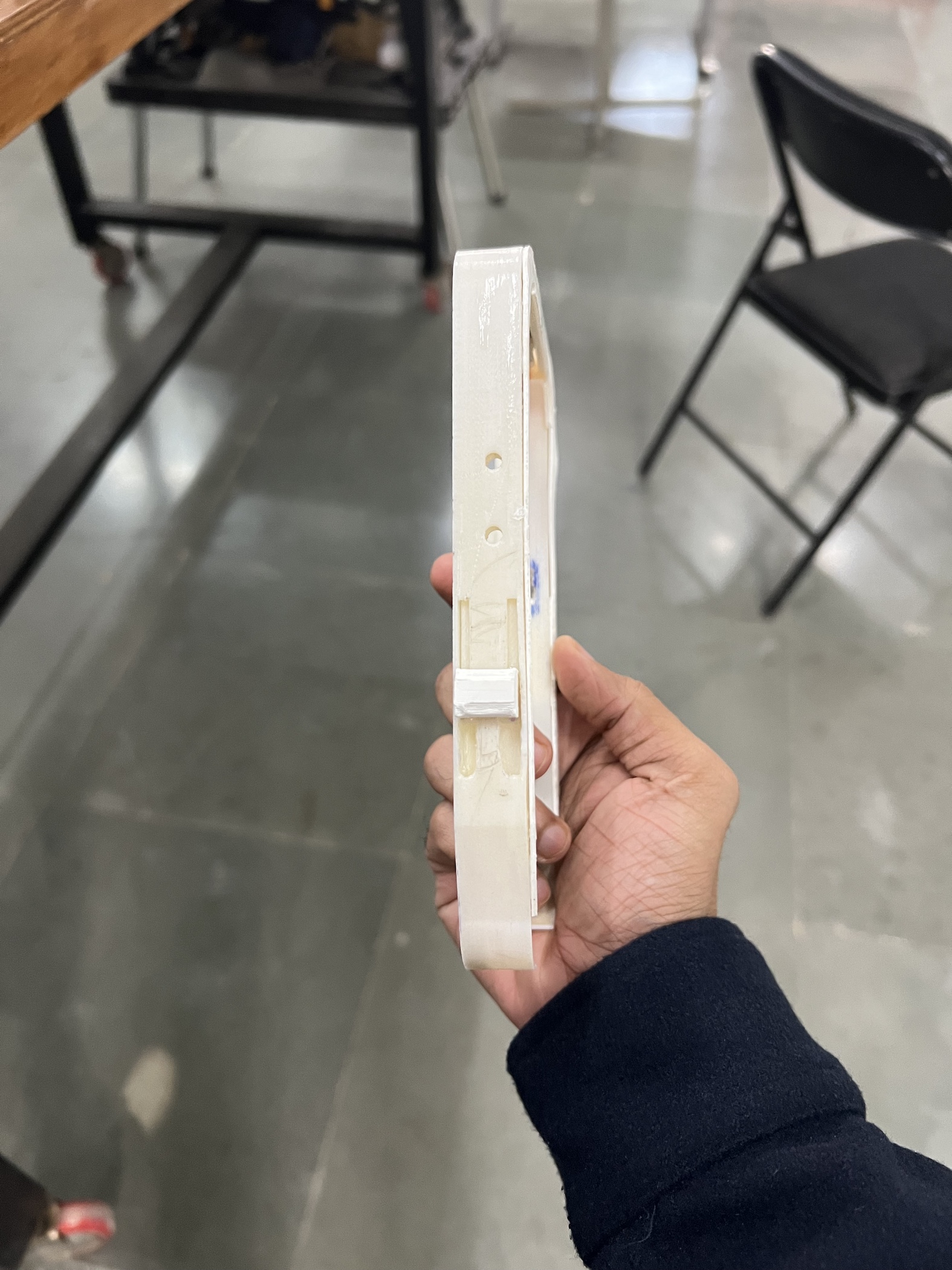
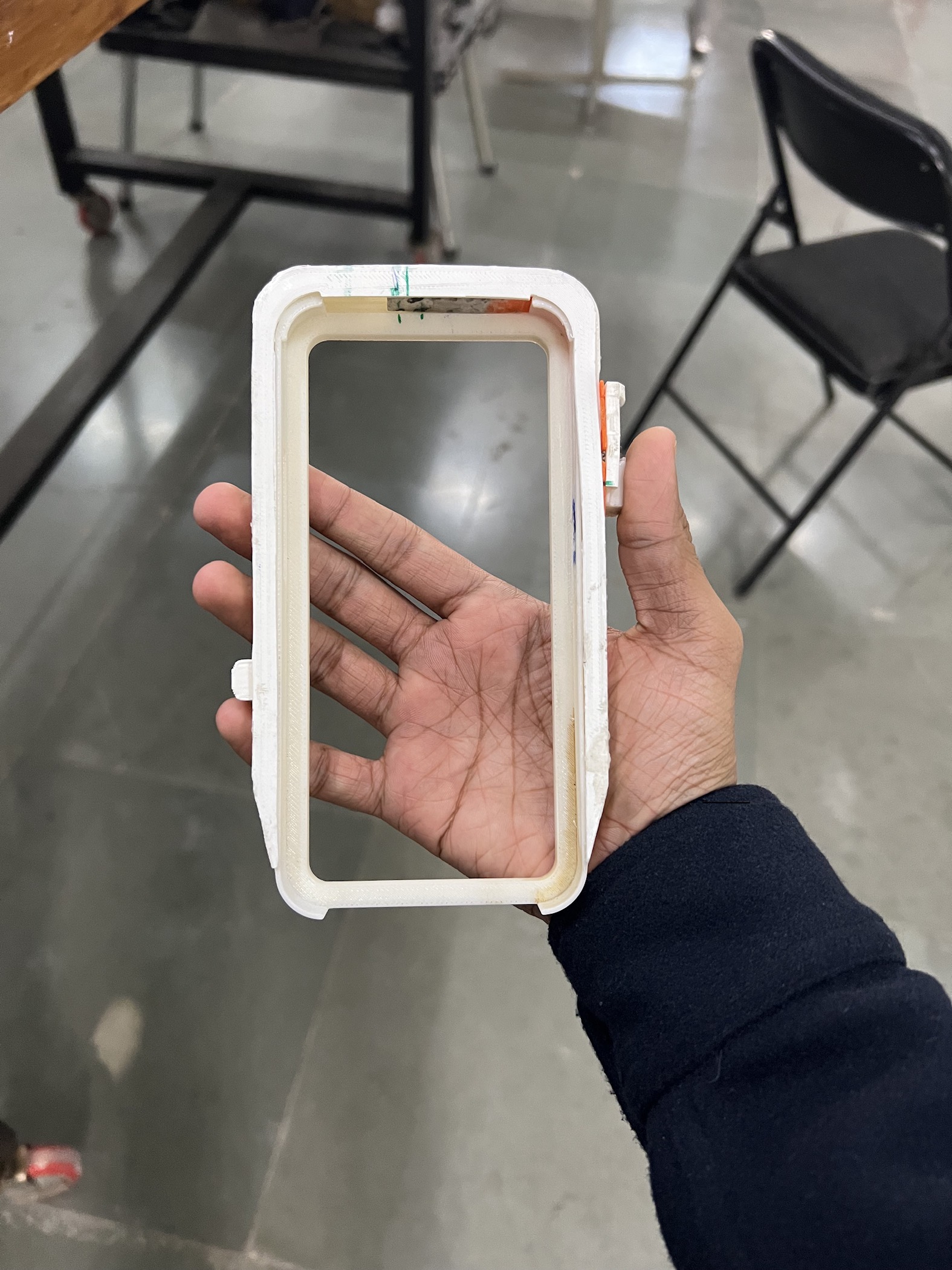



The framework has three distinct widgets, button, slider and rotary. Each widget has a metal alloy corresponding to it that moves as the user interacts with the widget. The disruption in magnetic field around the framework as user interacts with the widgets is captured using the magnetometer inside the smartphone.
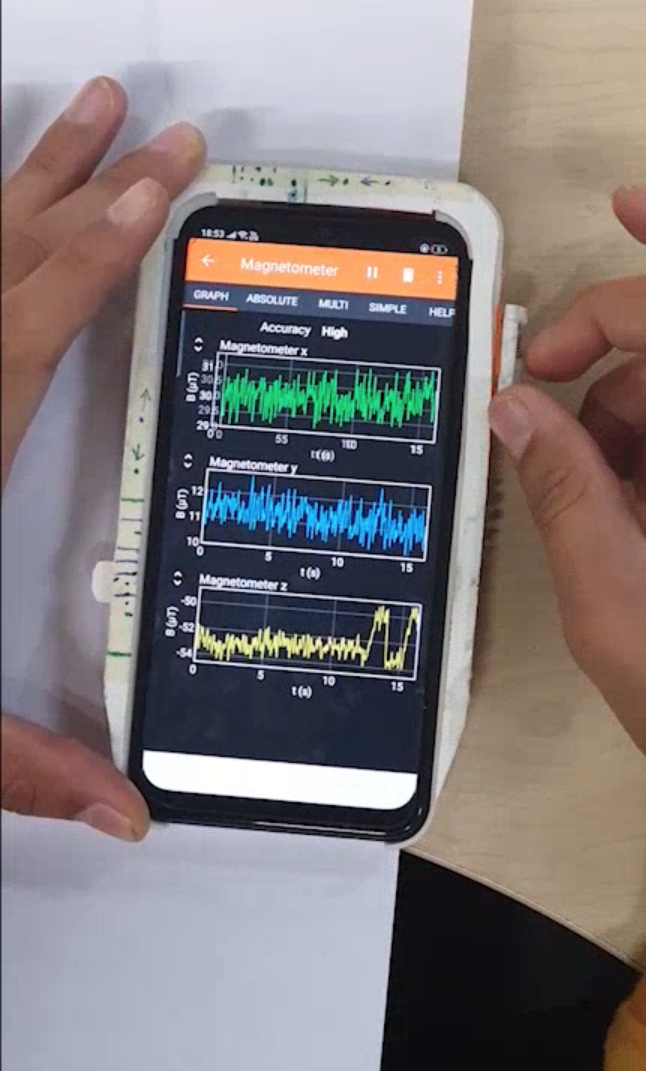
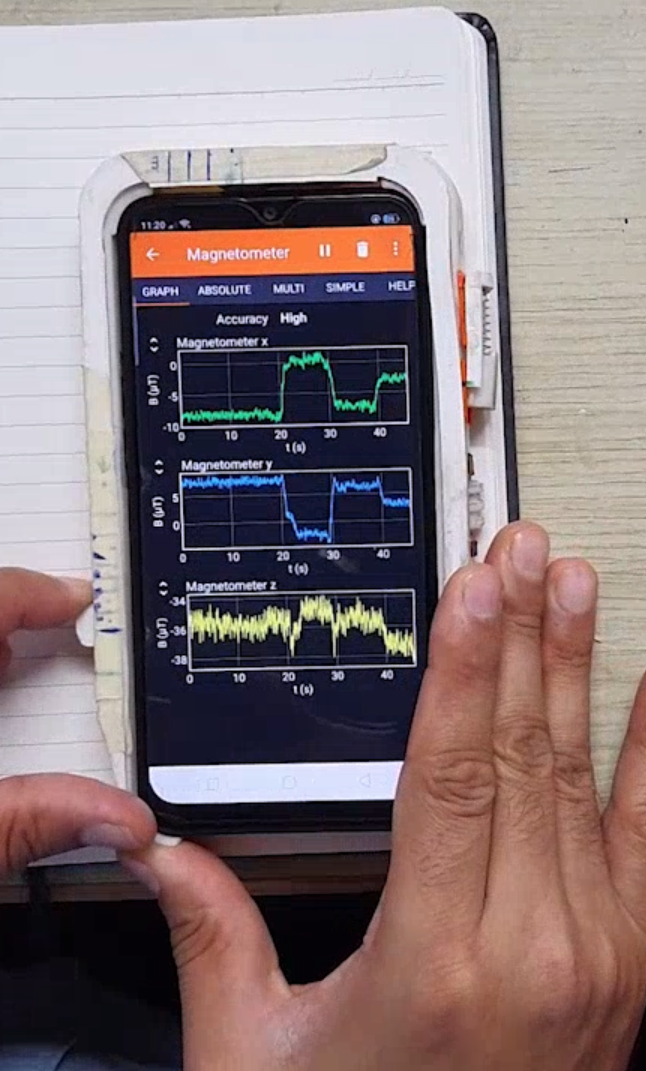
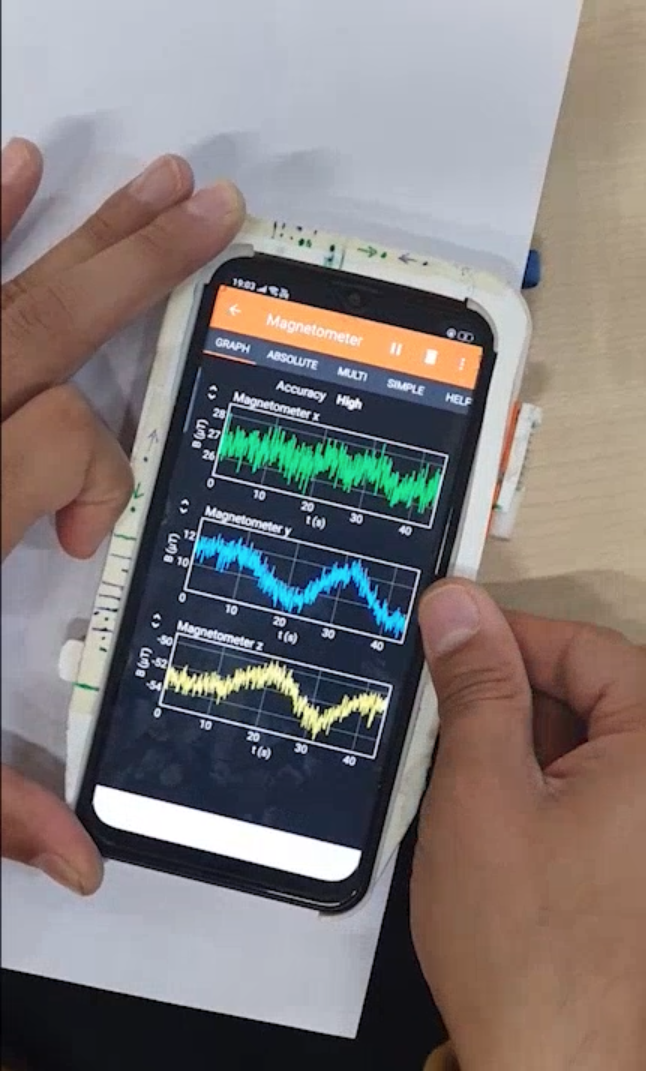
The signals recorded using the magnetomter are processed before being passed into the machine learning pipeline for widget prediction.
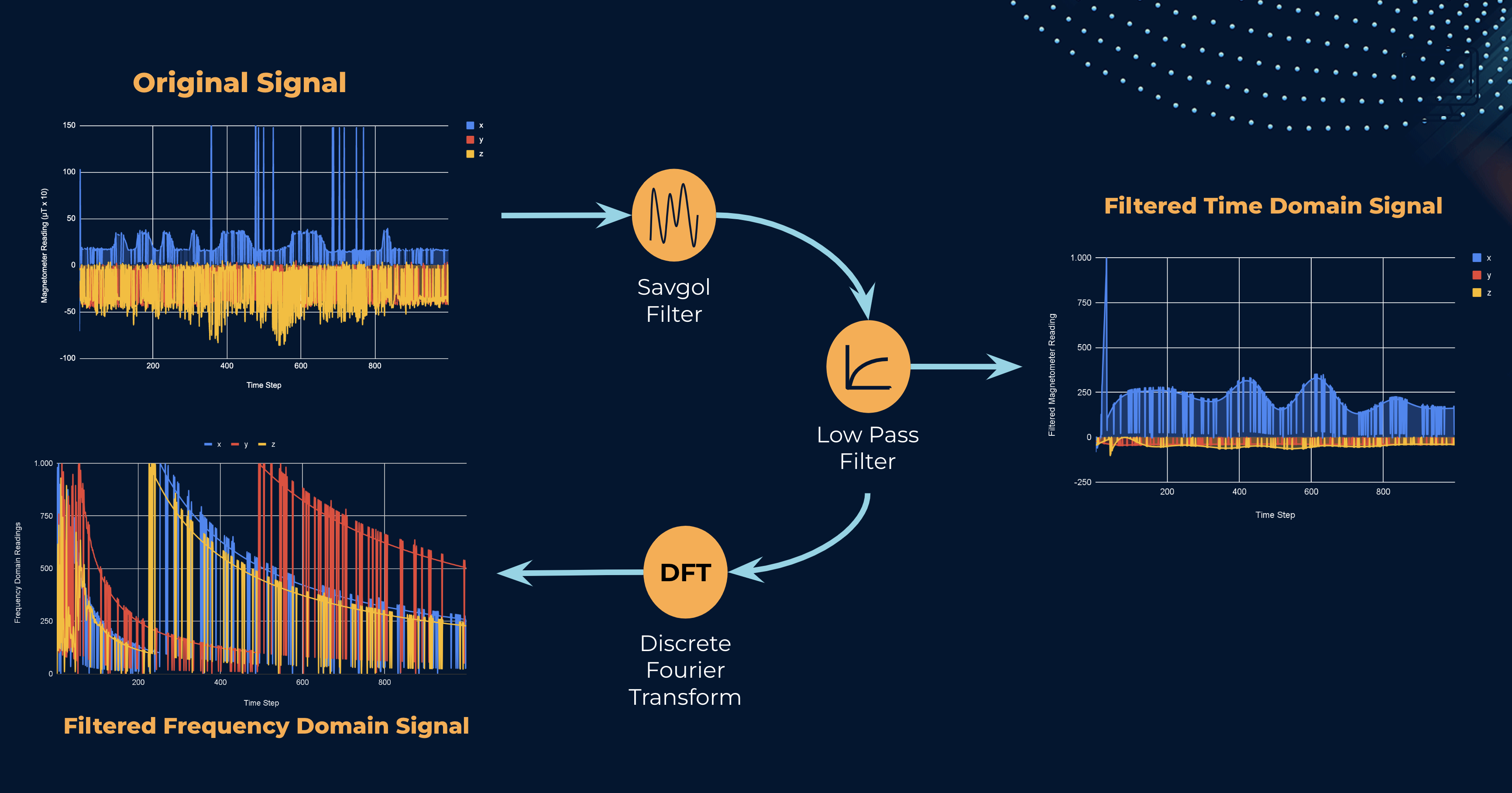
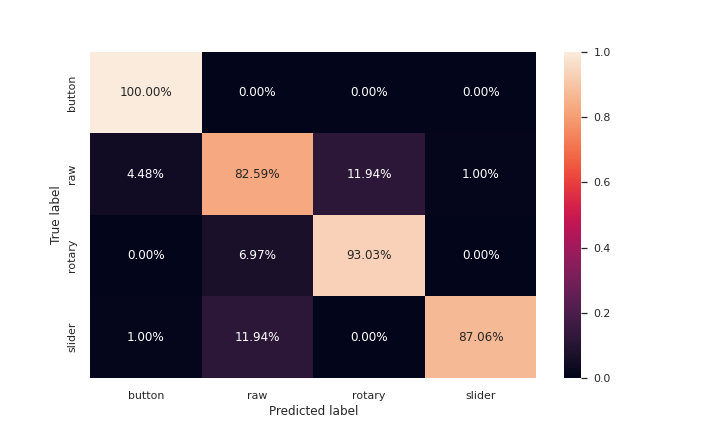
After testing various models using pycaret, following were the results for the best model, which was the Extra Trees classifer.